As first step, PVE-correction
can be performed for the presence of non-brain voxels…
(Two compartment method: parenchyma-CSF)
This approach,based on the use of anatomical images smoothed to the PET
resolution as correction factors, was first proposed for 2D-correction
of PET images [Videen et al,1988]
for CSF contribution only.(Two compartment method: parenchyma-CSF)
First the map of brain parenchyma (i.e. a segmented image where brain parenchyma voxels are set to 1, and 0 otherwise) is convoluted by the PSF of the scanner to provide the occupancy map of parenchyma (having values ranging from 0 to 1). The PET is divided by the occupancy map of the parenchyma and provides tracer concentration values for parenchyma voxel corrected from the spill-over effect.
The corrected parenchyma value is calculated as
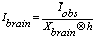
The division by the occupancy map (denominator), which is common to all voxel-based methods, can be regarded as the application of a recovery coefficient to the PET voxels for the correction of the spill-over effect.
This procedure was subsequently extended in 3D by Meltzer et al [1990]
MQ
| Home |